Are you ready to unlock the secrets of the real estate market and learn how to analyze deals like a pro? The real estate world can be a complex and competitive landscape, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can gain a significant advantage. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential skills to analyze deals, identify lucrative opportunities, and make informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting your real estate journey, this guide will provide valuable insights to help you navigate the market with confidence.
From understanding market trends to evaluating properties and negotiating contracts, we’ll delve into the crucial aspects of real estate analysis. We’ll cover essential concepts such as cash flow analysis, return on investment (ROI), and comparative market analysis (CMA), empowering you to make data-driven decisions. We’ll also explore innovative strategies and tools to streamline your analysis process, saving you time and effort.
Understanding the Basics of Real Estate Analysis
Real estate analysis is a crucial process for investors, developers, and anyone involved in the real estate market. It involves evaluating properties and projects to determine their financial viability, potential risks, and overall value. By conducting a thorough analysis, you can make informed decisions about buying, selling, investing, or developing real estate.
Key Components of Real Estate Analysis
Real estate analysis encompasses a wide range of factors, including:
- Market Analysis: Understanding the supply and demand dynamics of the local real estate market, including trends, demographics, and competition.
- Property Analysis: Evaluating the physical characteristics of a property, such as size, condition, location, and amenities.
- Financial Analysis: Assessing the financial performance of a property, including income, expenses, cash flow, and return on investment (ROI).
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks associated with a property or project, such as market fluctuations, environmental issues, or legal challenges.
Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques are used in real estate analysis, including:
- Financial Modeling: Creating spreadsheets or using software to project future income, expenses, and cash flows.
- Comparable Sales Analysis (CMA): Comparing the subject property to similar properties that have recently sold to determine its market value.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis: Estimating the present value of future cash flows from a property.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Examining how changes in key variables, such as interest rates or vacancy rates, can affect the overall financial performance of a property.
Benefits of Real Estate Analysis
Conducting a thorough real estate analysis offers numerous benefits, such as:
- Informed Decision-Making: By understanding the risks, potential returns, and overall value of a property, you can make more confident and informed investment decisions.
- Reduced Risk: Identifying potential risks early on allows you to mitigate them or make informed decisions to avoid them altogether.
- Enhanced Investment Performance: By identifying properties with strong financial performance and growth potential, you can maximize your investment returns.
- Improved Negotiation Skills: A solid understanding of real estate analysis empowers you to negotiate better prices and terms for your properties.
Key Financial Metrics to Evaluate
Financial metrics are crucial for understanding a company’s performance, profitability, and financial health. They provide insights into various aspects of the business, helping investors, analysts, and management make informed decisions.
Here are some key financial metrics to evaluate:
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
- Gross Profit Margin: This ratio shows the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It indicates the company’s efficiency in managing its direct costs.
- Operating Profit Margin: This ratio reveals the percentage of revenue left after deducting operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities. It reflects the company’s ability to control its operating costs.
- Net Profit Margin: This ratio represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest. It is a measure of overall profitability.
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations.
- Current Ratio: This ratio compares a company’s current assets (cash, accounts receivable, and inventory) to its current liabilities (accounts payable and short-term debt). A higher ratio indicates stronger liquidity.
- Quick Ratio: This ratio is similar to the current ratio but excludes inventory, which is considered less liquid. It provides a more conservative view of a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations.
- Cash Ratio: This ratio calculates the proportion of a company’s highly liquid assets (cash and cash equivalents) to its current liabilities. It reflects the company’s immediate ability to pay its debts.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio indicates the proportion of debt financing compared to equity financing. A higher ratio suggests a higher level of financial risk.
- Times Interest Earned Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its interest expenses with its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). A higher ratio indicates a stronger ability to service debt.
- Debt-to-Asset Ratio: This ratio calculates the proportion of a company’s assets financed by debt. A higher ratio suggests a higher level of financial leverage.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios measure how effectively a company utilizes its assets and resources.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: This ratio shows how quickly a company sells its inventory. A higher ratio suggests efficient inventory management.
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): This ratio measures the average number of days it takes a company to collect its receivables. A lower ratio indicates efficient collection processes.
- Asset Turnover Ratio: This ratio measures how efficiently a company utilizes its assets to generate revenue. A higher ratio indicates effective asset utilization.
Valuation Ratios
Valuation ratios compare a company’s market value to its financial performance. They provide insights into investor sentiment and the company’s intrinsic value.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: This ratio measures the market value of a company’s shares relative to its earnings per share. It reflects investor expectations for future earnings growth.
- Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio: This ratio compares a company’s market capitalization to its revenue. It is often used to value companies with high growth potential.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: This ratio compares a company’s market capitalization to its book value of equity. It indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of net assets.
By carefully analyzing these key financial metrics, investors, analysts, and management can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health, profitability, and future potential. This information can then be used to make informed investment decisions, assess company performance, and guide strategic planning.
Analyzing Property Value and Market Trends

Understanding property value and market trends is crucial for anyone involved in real estate, whether you’re a buyer, seller, investor, or simply a homeowner. By staying informed about the dynamics of the market, you can make well-informed decisions and optimize your investments.
Property value refers to the estimated worth of a property, taking into account factors such as location, size, condition, amenities, and market demand. This value can fluctuate over time due to various factors, including economic conditions, interest rates, and local market trends.
Factors Influencing Property Value
Several factors influence the value of a property. These include:
- Location: Properties in desirable neighborhoods with good schools, amenities, and access to transportation tend to command higher prices.
- Size and Layout: The size of the property, number of bedrooms and bathrooms, and overall layout significantly impact its value.
- Condition: The condition of the property, including its age, renovations, and maintenance, plays a crucial role in determining its value.
- Amenities: Features like swimming pools, garages, and landscaped yards can increase property value.
- Market Demand: The demand for properties in a particular area can drive prices up or down. Factors like population growth, economic activity, and employment opportunities influence market demand.
Market Trends
Market trends refer to the overall patterns and fluctuations in the real estate market. These trends can be influenced by economic conditions, government policies, and other factors. Understanding market trends can help you identify opportunities and make informed decisions.
Analyzing Market Data
To analyze property value and market trends, you can utilize various resources, including:
- Real Estate Websites: Websites like Zillow, Redfin, and Realtor.com provide data on property values, sales history, and market trends.
- Real Estate Agents: Experienced real estate agents have access to local market data and can offer insights into property values and trends.
- Appraisal Reports: Professional appraisals provide an objective assessment of a property’s value.
- Government Data: Government agencies often release data on housing starts, sales, and price trends.
By analyzing market data and staying informed about the factors influencing property value, you can make sound decisions and navigate the real estate market with confidence.
Calculating Cash Flow and Return on Investment (ROI)

Cash flow and return on investment (ROI) are two of the most important metrics for any business. Cash flow is the amount of money that flows into and out of a business over a period of time. It is a measure of a business’s liquidity, or its ability to meet its short-term financial obligations. ROI, on the other hand, is a measure of the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by dividing the net profit by the cost of the investment. Both metrics are essential for businesses to understand their financial health and make informed decisions about their operations.
Calculating Cash Flow
To calculate cash flow, you need to track the following:
- Cash inflows: This includes all the money that comes into your business, such as sales revenue, loan proceeds, and investments.
- Cash outflows: This includes all the money that goes out of your business, such as expenses, debt repayments, and investments.
Once you have tracked your cash inflows and outflows, you can calculate your cash flow by subtracting your total cash outflows from your total cash inflows. The formula for calculating cash flow is as follows:
Cash Flow = Cash Inflows – Cash Outflows
Calculating ROI
To calculate ROI, you need to know the following:
- Net Profit: This is the profit that you make after deducting all your expenses from your revenue.
- Cost of Investment: This is the amount of money that you invested in the project or asset.
Once you have these two numbers, you can calculate your ROI using the following formula:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
For example, if you invest $10,000 in a project and make a net profit of $2,000, your ROI would be:
ROI = ($2,000 / $10,000) x 100 = 20%
Using Cash Flow and ROI
Cash flow and ROI are important metrics for businesses of all sizes. By tracking and analyzing these metrics, businesses can:
- Identify potential financial problems: Businesses with low cash flow may have difficulty meeting their financial obligations. Businesses with low ROI may be investing in unprofitable projects.
- Make informed decisions about their operations: Businesses can use cash flow and ROI data to make decisions about pricing, marketing, and investments.
- Improve their financial performance: Businesses can use cash flow and ROI data to identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and profitability.
Assessing Property Condition and Potential Risks
When considering the purchase of a property, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough assessment of its condition and potential risks. This involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing both internal and external factors. By diligently evaluating these aspects, potential buyers can gain valuable insights into the property’s overall health, potential liabilities, and potential return on investment.
A fundamental step is conducting a comprehensive home inspection. This involves engaging a qualified professional to scrutinize the property’s structure, systems, and components. The inspector will examine areas such as the foundation, roof, plumbing, electrical wiring, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), and appliances. Their findings are documented in a detailed report that outlines any existing or potential problems, including their severity and recommended solutions.
Beyond the physical structure, it’s equally important to assess the property’s surrounding environment. This includes factors like neighborhood amenities, proximity to schools, parks, and public transportation, as well as the prevalence of noise, crime, and environmental hazards. Understanding these external factors can significantly influence the property’s desirability, potential for appreciation, and overall quality of life for future residents.
In addition to a home inspection, it’s prudent to consider obtaining other specialized evaluations depending on the property’s specific characteristics. For example, properties located in areas prone to natural disasters may require a geotechnical assessment to assess the risk of earthquakes, landslides, or flooding. Similarly, older properties might benefit from a radon test, particularly in areas with elevated radon levels.
Furthermore, it’s wise to explore the property’s history. Checking for previous renovations, repairs, or upgrades can provide insights into potential issues or areas of neglect. Consulting public records, such as building permits and property tax assessments, can also shed light on the property’s history and potential legal liabilities.
By diligently assessing a property’s condition and potential risks through a comprehensive evaluation process, potential buyers can make more informed decisions, minimize unforeseen expenses, and ensure a smooth transition into their new home.
Due Diligence Checklist for Real Estate Investors

Investing in real estate can be a lucrative venture, but it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence before making any commitments. Due diligence involves carefully scrutinizing a property and its related factors to assess its potential risks and rewards. This checklist will guide you through the essential steps to ensure a well-informed investment decision.
1. Property Inspection
A comprehensive property inspection is paramount. It’s recommended to hire a qualified inspector to assess the condition of the property’s structure, systems, and amenities. This includes:
- Foundation: Inspecting the foundation for cracks, settling, or other structural issues.
- Roofing: Checking the roof for leaks, damage, and overall condition.
- Plumbing and Electrical: Evaluating the condition of plumbing and electrical systems, including wiring, fixtures, and appliances.
- HVAC: Assessing the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system’s functionality and efficiency.
- Pest Inspection: Identifying any evidence of pests and their potential impact on the property.
2. Title Search and Review
A thorough title search is vital to ensure clear ownership of the property. It reveals any existing liens, encumbrances, or other claims that could affect your rights as a buyer. This process typically involves:
- Title Insurance: Obtaining title insurance protects you from potential financial losses related to title defects.
- Chain of Title: Verifying the history of ownership and identifying any potential legal issues.
- Liens and Encumbrances: Examining any outstanding liens, mortgages, or other encumbrances on the property.
3. Financial Analysis
A detailed financial analysis is crucial to evaluate the investment’s viability. It includes:
- Income and Expenses: Estimating potential rental income and projected operating expenses, such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs.
- Cash Flow: Determining the net cash flow after deducting expenses from income.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating the expected return on investment, considering the purchase price, renovation costs, and potential appreciation.
4. Market Research
Thorough market research is essential to assess the property’s value and potential rental demand. This involves:
- Neighborhood Analysis: Evaluating the local market conditions, including supply and demand, crime rates, and school districts.
- Rental Market Trends: Researching current and projected rental rates, occupancy levels, and tenant demographics.
- Competition: Assessing the competitive landscape, including similar properties in the area.
5. Zoning and Building Codes
Understanding zoning regulations and building codes is critical to ensure the property’s legal use and compliance. It involves:
- Zoning Compliance: Verifying that the property’s current use aligns with local zoning regulations.
- Building Code Requirements: Reviewing building code requirements for any proposed renovations or alterations.
- Permitting Process: Understanding the permitting process for any future construction or renovations.
6. Environmental Due Diligence
For certain properties, environmental due diligence is essential to identify potential risks, such as:
- Environmental Hazards: Assessing the presence of hazardous materials, such as asbestos, lead paint, or mold.
- Environmental Regulations: Understanding environmental regulations that may affect the property, such as those related to wetlands or hazardous waste disposal.
- Environmental Site Assessments (ESAs): Conducting ESAs to identify and assess potential environmental liabilities.
7. Legal Review
Before signing any contracts, it’s crucial to have a real estate attorney review the purchase agreement and other relevant documents. This includes:
- Contract Review: Ensuring the purchase agreement’s terms are favorable and protect your interests.
- Title Examination: Examining the title documents for any potential issues or encumbrances.
- Disclosure Requirements: Verifying that the seller has fulfilled all disclosure requirements.
8. Insurance Review
Understanding the property’s insurance needs is crucial to protect your investment. This involves:
- Property Insurance: Obtaining adequate property insurance coverage for the property.
- Liability Insurance: Assessing the need for liability insurance to cover potential legal claims.
- Flood Insurance: Determining if flood insurance is necessary based on the property’s location.
9. Communication and Documentation
Maintaining clear communication with the seller, inspector, and other professionals is essential. It’s also crucial to document all inspections, reports, and agreements to have a comprehensive record of the due diligence process.
By meticulously following this due diligence checklist, real estate investors can significantly reduce risks and enhance their chances of making sound investment decisions. Remember, due diligence is not a one-time event but an ongoing process throughout the investment lifecycle.
Negotiating Strategies for Successful Deals

Negotiation is an essential part of life, whether it’s in our personal or professional lives. It’s a skill that can be learned and honed over time, and it’s crucial to be able to negotiate effectively to achieve successful outcomes. Whether you’re negotiating a salary, a contract, or a purchase, understanding the key principles and strategies can significantly enhance your chances of getting the best possible deal.
The first step in successful negotiation is to thoroughly prepare. This involves understanding your own needs and goals, researching the other party’s position, and anticipating potential obstacles. Defining your bottom line and walking away point is crucial, as it provides a clear framework for your negotiation. When you’re well-prepared, you can approach the negotiation process with confidence and clarity.
Next, it’s essential to build rapport and trust with the other party. This involves active listening, empathizing with their perspective, and fostering a positive and collaborative atmosphere. By creating a sense of mutual respect and understanding, you can lay the groundwork for a mutually beneficial agreement.
Once you’ve established a foundation, it’s time to present your case persuasively. This involves clearly articulating your needs and goals, supporting your arguments with relevant data and evidence, and effectively communicating the value you bring to the table. Be prepared to negotiate on multiple issues and be flexible in your approach, as compromise is often necessary to reach a satisfactory outcome.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to be aware of potential pitfalls and leverage them strategically. Recognizing and addressing the other party’s concerns, managing expectations realistically, and being adaptable in your strategies can help you navigate challenging situations effectively. It’s also essential to be mindful of potential power imbalances and leverage your strengths accordingly.
Finally, remember that successful negotiation is not about winning at all costs. It’s about finding a solution that works for both parties involved. This involves being open to compromise, exploring creative solutions, and ultimately, achieving a win-win outcome. By fostering a spirit of collaboration and seeking mutually beneficial solutions, you can achieve lasting success in your negotiations.
Legal and Tax Considerations
Before you launch your business, it is crucial to understand the legal and tax implications involved. This includes choosing the right business structure, obtaining necessary licenses and permits, complying with tax regulations, and safeguarding your intellectual property. Let’s delve into these considerations in detail.
Business Structure
The legal structure of your business will have a significant impact on your liability, taxation, and administrative burden. Common business structures include:
- Sole Proprietorship: This is the simplest structure, where the business is owned and operated by one person. The owner is personally liable for all business debts.
- Partnership: Two or more individuals agree to share in the profits and losses of a business. Partners can be personally liable for business debts.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): This structure offers limited liability protection, meaning that the personal assets of the owners are protected from business debts. However, LLCs can be more complex to set up and maintain than sole proprietorships or partnerships.
- Corporation: A corporation is a separate legal entity from its owners, providing the highest level of liability protection. However, corporations are subject to double taxation on profits (at the corporate level and again at the shareholder level).
Choosing the right structure depends on factors such as the nature of your business, your risk tolerance, and your tax situation. It is advisable to consult with an attorney or accountant to determine the most suitable structure for your specific needs.
Licensing and Permits
Depending on your industry and location, you may need to obtain various licenses and permits to operate legally. These can include:
- Business license: A general license required by most municipalities for businesses to operate within their jurisdiction.
- Professional licenses: Licenses required for certain professions, such as doctors, lawyers, and accountants.
- Industry-specific permits: Permits required for certain industries, such as food service or construction.
- Environmental permits: Permits required for businesses that may impact the environment, such as manufacturing or waste disposal.
Failing to obtain necessary licenses and permits can result in fines, penalties, and even closure of your business. It is crucial to research and secure all required licenses and permits before you open your doors.
Tax Regulations
Understanding tax regulations is crucial for any business owner. This includes:
- Income tax: Businesses are required to pay income tax on their profits. The tax rate depends on the business structure and other factors.
- Sales tax: Many states and local governments require businesses to collect and remit sales tax on goods and services sold. The sales tax rate varies by location.
- Payroll tax: Businesses are required to withhold payroll taxes from employee wages, including Social Security, Medicare, and federal and state income tax.
- Property tax: Businesses may be required to pay property tax on real estate they own or lease.
Keeping accurate records and filing tax returns on time is essential to avoid penalties and legal issues. Consulting with a tax professional can help you navigate the complex world of tax regulations.
Intellectual Property
Protecting your intellectual property is crucial for any business, especially those involved in innovation or creativity. Forms of intellectual property include:
- Trademarks: Protect brand names, logos, and slogans.
- Patents: Protect inventions and processes.
- Copyrights: Protect original works of authorship, such as books, music, and software.
- Trade secrets: Protect confidential information that provides a competitive advantage.
Taking steps to protect your intellectual property can help you prevent competitors from copying your ideas and ensure that you have exclusive rights to your creations. Consulting with an intellectual property attorney can help you navigate the legal process of registering and enforcing your intellectual property rights.
Tools and Resources for Real Estate Analysis

Real estate analysis is a crucial aspect of making informed investment decisions. By analyzing various factors, investors can identify profitable opportunities and mitigate risks. To facilitate this process, a wide array of tools and resources are available, each offering unique insights and functionalities.
One of the essential tools for real estate analysis is real estate databases. These databases provide comprehensive information on property listings, sales history, market trends, and demographics. Platforms such as Zillow, Redfin, and Trulia offer valuable data and analytical features, enabling investors to track market fluctuations and identify undervalued properties.
For investors seeking a deeper understanding of financial metrics, financial modeling tools are indispensable. Excel spreadsheets, dedicated software like Argus, and online platforms like CoStar Analytics allow investors to create detailed financial models that analyze property performance, cash flow projections, and return on investment (ROI).
Another valuable resource is real estate research reports. These reports, published by reputable firms and institutions, provide in-depth analysis of specific markets, property types, and economic trends. Reports from organizations like the National Association of Realtors (NAR), CoreLogic, and Moody’s Analytics can offer valuable insights and market intelligence.
In addition to traditional tools, online data visualization platforms have emerged as powerful resources for real estate analysis. Platforms like Tableau and Power BI enable investors to create interactive dashboards that visualize complex data sets, revealing trends and patterns that might otherwise be overlooked.
For investors interested in leveraging the power of artificial intelligence (AI), AI-powered real estate analysis tools are becoming increasingly prevalent. These tools utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, identify investment opportunities, and predict market behavior with greater accuracy.
Ultimately, the best tools and resources for real estate analysis depend on the specific needs and goals of the investor. By utilizing a combination of these resources, investors can gain a comprehensive understanding of the market, identify promising opportunities, and make informed decisions to maximize their returns.
Case Study: Analyzing a Rental Property Deal
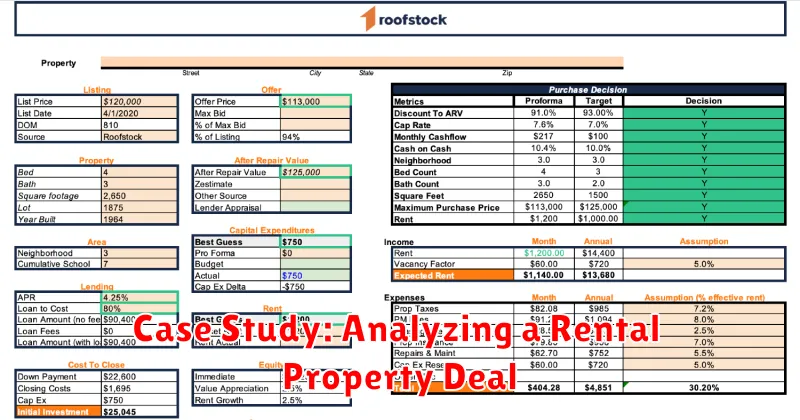
In the world of real estate investing, analyzing potential deals is crucial. This case study dives into a real-life scenario, examining the financial aspects of a rental property deal. We’ll analyze the numbers, consider the risks, and determine if this deal is a wise investment.
The Property
The property in question is a single-family home located in a growing suburban area. It boasts 3 bedrooms, 2 bathrooms, and a spacious backyard. The purchase price is $300,000.
The Finances
Here’s a breakdown of the financial aspects of the deal:
- Down Payment: 20% of the purchase price, amounting to $60,000.
- Mortgage: A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 5% interest, resulting in a monthly payment of $1,610.
- Property Taxes: Estimated at $3,000 per year.
- Insurance: Estimated at $1,200 per year.
- Estimated Monthly Expenses: $1,610 (mortgage) + $250 (taxes and insurance) = $1,860.
Rental Income
The property is expected to generate a monthly rental income of $2,500. This is based on market research and comparable rentals in the area.
Analyzing the Numbers
Let’s analyze the profitability of this investment:
- Gross Rental Income: $2,500 per month x 12 months = $30,000 per year.
- Total Annual Expenses: $1,860 per month x 12 months = $22,320 per year.
- Net Operating Income (NOI): $30,000 (gross income) – $22,320 (expenses) = $7,680 per year.
- Cap Rate: $7,680 (NOI) / $300,000 (purchase price) = 2.56%.
A cap rate is a measure of a property’s profitability. It reflects the annual return on investment based on the property’s net operating income. In this case, the cap rate of 2.56% is considered below average for residential rental properties. This suggests that the potential return on investment might not be as high as other available opportunities.
Risks and Considerations
Investing in rental properties always involves inherent risks. Here are some key considerations for this deal:
- Vacancy Rates: Even in a growing area, there’s always a risk of vacancies between tenants. This could impact rental income and overall profitability.
- Tenant Issues: Dealing with difficult tenants, property damage, or late rent payments can be stressful and costly.
- Market Fluctuations: Real estate markets can fluctuate, impacting property values and rental rates.
- Maintenance Costs: Unexpected repairs or renovations can eat into profits, especially as the property ages.
Mistakes to Avoid When Analyzing Deals
Deal analysis is a crucial part of any business, whether you’re a seasoned investor or a startup founder. It’s the process of carefully examining the potential benefits and risks of a transaction to determine whether it aligns with your goals and objectives. While deal analysis can be a complex undertaking, it’s essential to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to costly errors and missed opportunities. Here are some key mistakes to avoid when analyzing deals:
1. Failing to Define Clear Objectives
Before diving into the details of a potential deal, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your goals. What are you hoping to achieve through this transaction? Are you looking to acquire new customers, enter a new market, or simply increase your revenue? Defining your objectives upfront will provide a framework for evaluating the deal’s potential and determining whether it aligns with your overall business strategy.
2. Neglecting Due Diligence
Due diligence is the process of thoroughly investigating a potential deal to uncover any potential risks or red flags. This involves examining financial statements, reviewing contracts, and conducting background checks on the parties involved. Skipping due diligence can lead to unpleasant surprises down the road, so it’s crucial to take the time to perform this essential step.
3. Ignoring Market Analysis
Understanding the competitive landscape and market trends is essential for making informed decisions. Before committing to a deal, consider the industry’s overall health, the competitive landscape, and any potential disruptors that could impact the deal’s long-term viability.
4. Overlooking the Legal Aspects
The legal framework surrounding a deal can be complex, and overlooking important legal considerations can have significant repercussions. Make sure you have a legal team that can thoroughly review the terms of the deal and ensure it complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
5. Failing to Consider the Exit Strategy
While it’s essential to focus on the immediate benefits of a deal, it’s also important to consider your exit strategy. How will you eventually exit the deal? What are the potential risks and rewards associated with different exit options? Having a clear exit strategy in place will help you manage the deal’s long-term implications.
6. Falling into the Trap of “Sunk Cost”
You may have invested significant time and resources into a particular deal, but it’s crucial to remember that sunk costs are irrelevant to future decisions. If the deal no longer makes strategic sense, don’t be afraid to walk away, even if it means admitting you made a mistake.
7. Neglecting to Plan for Integration
If the deal involves acquiring another company or merging with another entity, it’s essential to plan for a smooth integration process. This includes identifying potential areas of conflict, developing communication strategies, and ensuring that the combined entity can operate efficiently.

