The financial landscape is rapidly evolving, with blockchain technology emerging as a transformative force. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the impact of blockchain on the future of finance is undeniable. As we step into [Current Year], several exciting blockchain trends are poised to reshape the industry, creating new opportunities and challenges for businesses and individuals alike.
In this article, we’ll delve into the top blockchain trends to watch in [Current Year], exploring their potential implications for the financial world. Get ready to discover how decentralized finance (DeFi) is expanding beyond lending and borrowing, the rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and the exciting possibilities of stablecoins. We’ll also examine the role of NFTs beyond digital art and the growing importance of interoperability between blockchain networks. By staying informed about these trends, you can navigate the future of finance with confidence and seize the opportunities presented by this disruptive technology.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Revolution
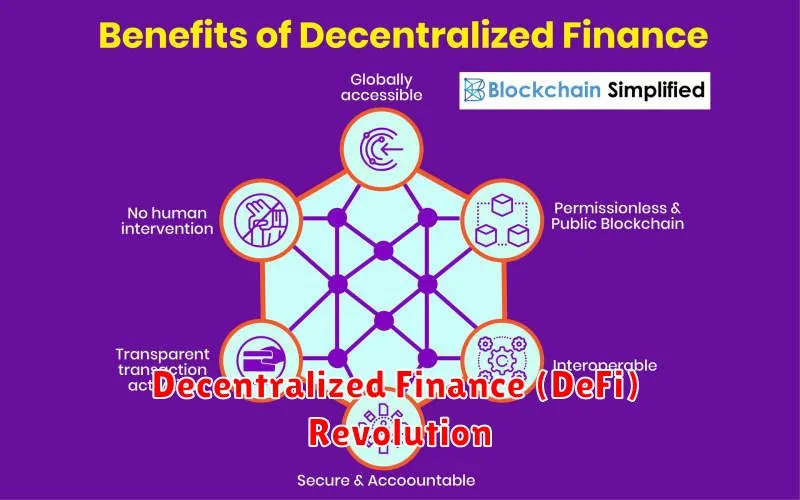
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a rapidly evolving sector of the cryptocurrency ecosystem that aims to revolutionize traditional financial services by leveraging blockchain technology. DeFi applications are built on decentralized networks, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks, brokers, and exchanges. This allows for greater transparency, accessibility, and control over financial assets.
One of the key pillars of DeFi is smart contracts, self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. Smart contracts automate financial transactions, ensuring that agreements are executed precisely and transparently. This eliminates the risk of fraud or manipulation associated with traditional financial systems.
Another important aspect of DeFi is the use of stablecoins. Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the US dollar, minimizing price volatility and providing a more reliable store of value. This stability is crucial for various DeFi applications, such as lending and borrowing.
DeFi applications offer a wide range of financial services, including:
- Lending and Borrowing: Users can lend their crypto assets to earn interest or borrow crypto assets by providing collateral.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Users can trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without the need for a central intermediary.
- Yield Farming: Users can stake their crypto assets in liquidity pools to earn rewards by providing liquidity for trading.
- Insurance: DeFi protocols offer insurance against various risks, such as smart contract vulnerabilities and price fluctuations.
The DeFi revolution has the potential to democratize finance, empowering individuals to control their own financial destinies. However, it’s essential to acknowledge the risks associated with this emerging technology, such as smart contract vulnerabilities and price volatility. As DeFi continues to evolve, it’s crucial to stay informed and exercise caution when interacting with DeFi applications.
The Rise of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)

The world of digital assets is rapidly evolving, and one of the most exciting developments in recent years has been the emergence of non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These unique digital assets have taken the world by storm, capturing the attention of artists, collectors, and investors alike.
But what exactly are NFTs, and why are they generating so much buzz?
Understanding NFTs
At its core, an NFT is a unit of data stored on a blockchain, a distributed ledger that records transactions and ensures their authenticity. Unlike traditional digital assets, which can be easily copied and replicated, NFTs are one-of-a-kind and indivisible. This uniqueness is what makes them so valuable.
Think of an NFT as a digital certificate of ownership for a unique asset, whether it’s a piece of digital art, a collectible item, or even a virtual world item. This certificate is recorded on the blockchain, making it transparent and tamper-proof.
The Power of NFTs
NFTs have the potential to revolutionize various industries, from art and entertainment to gaming and finance. Here are some of their key benefits:
- Ownership and Authenticity: NFTs provide irrefutable proof of ownership, eliminating the risk of counterfeiting and ensuring the authenticity of digital assets.
- Scarcity and Value: NFTs can be created in limited quantities, creating scarcity and increasing their value. This is particularly appealing to collectors.
- New Revenue Streams: NFTs allow artists and creators to monetize their work directly, without relying on intermediaries or platforms.
- Increased Accessibility: NFTs can be traded and exchanged on decentralized marketplaces, making them accessible to a wider audience.
Examples of NFTs
NFTs have already made a significant impact in various sectors. Here are some notable examples:
- Digital Art: Artists like Beeple and Grimes have sold their digital art as NFTs for millions of dollars, attracting both traditional art collectors and new entrants to the market.
- Gaming: NFTs are being used to create in-game items, virtual land, and other assets that can be traded and owned by players.
- Collectibles: NFTs are transforming the world of collectibles, allowing fans to own unique digital versions of their favorite sports cards, trading cards, and other memorabilia.
- Music: Musicians are using NFTs to sell exclusive tracks, albums, and even fan experiences.
The Future of NFTs
While still in its early stages, the NFT market is growing at an astonishing pace. As the technology matures and more use cases emerge, NFTs are poised to have a profound impact on the digital economy. From revolutionizing the way we create, own, and interact with digital assets to unlocking new possibilities for businesses and individuals, the future of NFTs holds immense potential.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and Their Implications

The emergence of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) has sparked intense debate and speculation about their potential impact on the global financial landscape. CBDCs, essentially digital versions of fiat currencies issued by central banks, represent a significant paradigm shift in monetary policy and financial technology. This article delves into the intricacies of CBDCs, exploring their potential benefits, challenges, and implications for various stakeholders.
Understanding CBDCs
Central banks around the world are actively exploring the development and implementation of CBDCs. While their specific designs may vary, the core concept involves creating a digital form of a country’s currency, directly controlled and managed by the central bank. This digital currency would coexist alongside existing physical currency and digital payment systems, potentially transforming the way individuals, businesses, and governments transact.
Potential Benefits of CBDCs
The potential benefits of CBDCs are multifaceted and encompass various aspects of the financial system:
-
Enhanced Payment Efficiency: CBDCs offer the potential for faster, cheaper, and more secure payments, both domestically and internationally.
-
Financial Inclusion: CBDCs can provide financial services to underserved populations, including those without access to traditional banking services.
-
Improved Monetary Policy: CBDCs could potentially enable central banks to implement monetary policy more effectively and efficiently.
-
Reduced Risk: CBDCs could help mitigate risks associated with traditional financial systems, such as fraud and money laundering.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of CBDCs are compelling, there are also significant challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
-
Privacy Concerns: The introduction of CBDCs raises concerns about the potential for increased government surveillance and data privacy infringement.
-
Cybersecurity Risks: CBDCs, being digital, are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could have severe consequences for the financial system.
-
Impact on Financial Institutions: The widespread adoption of CBDCs could potentially disrupt traditional financial institutions and their business models.
-
International Coordination: The global adoption of CBDCs would necessitate significant international coordination to ensure interoperability and avoid fragmentation.
Implications for Various Stakeholders
The introduction of CBDCs has far-reaching implications for various stakeholders, including:
-
Central Banks: CBDCs provide central banks with greater control over the money supply and the ability to conduct monetary policy more effectively.
-
Financial Institutions: CBDCs could potentially disrupt the business models of traditional financial institutions, particularly in payments and settlements.
-
Businesses: CBDCs could enable businesses to make faster, cheaper, and more secure payments, potentially leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness.
-
Consumers: CBDCs could provide consumers with greater access to financial services, lower transaction fees, and increased convenience.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
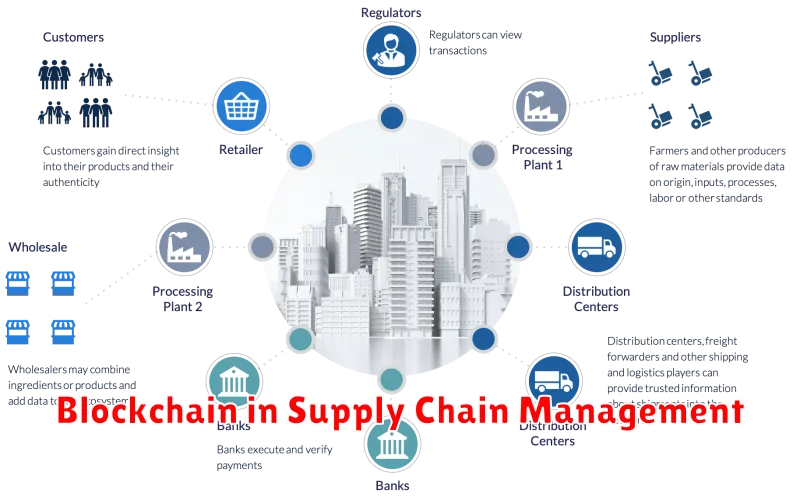
In the modern business landscape, supply chain management is a critical function that significantly impacts profitability and customer satisfaction. As businesses strive for greater transparency, efficiency, and security, blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative solution for revolutionizing supply chain operations. This article will delve into the key benefits of blockchain in supply chain management, explore its real-world applications, and examine the potential challenges and future trends in this exciting space.
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records and shares information securely and transparently across a network of computers. Each transaction is encrypted and added to a chain of blocks, creating an immutable and auditable record. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, fostering trust and collaboration among all participants in the supply chain.
The adoption of blockchain technology in supply chain management offers several compelling benefits:
Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods as they move through the supply chain, from origin to destination. This transparency allows businesses to monitor product movements, identify potential delays or disruptions, and ensure the authenticity of goods. For example, consumers can use blockchain to verify the origin and journey of products, gaining greater confidence in the quality and sustainability of their purchases.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
By streamlining processes and reducing administrative burdens, blockchain can significantly enhance supply chain efficiency. Automated data sharing and recordkeeping eliminate manual tasks, reduce errors, and accelerate transactions. This improved efficiency translates into cost savings for businesses and faster delivery times for customers.
Increased Security and Trust
The decentralized and tamper-proof nature of blockchain provides unparalleled security for supply chain data. Every transaction is recorded and encrypted, making it virtually impossible to alter or forge records. This immutability fosters trust among all parties involved, reducing fraud and counterfeiting risks.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Blockchain can automate complex supply chain processes through the use of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts define the terms and conditions of agreements between parties, ensuring automatic execution and eliminating the need for manual intervention. This automation simplifies transactions, reduces delays, and enhances overall efficiency.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is finding its way into diverse industries, revolutionizing supply chain operations across various sectors:
- Food and Beverage: Blockchain can track the journey of food products, from farm to table, ensuring food safety, traceability, and consumer confidence.
- Pharmaceuticals: Blockchain is crucial for maintaining the integrity and authenticity of pharmaceutical products, combating counterfeit medications, and ensuring patient safety.
- Manufacturing: Blockchain can streamline the production process, track materials and components, and improve inventory management in complex manufacturing operations.
- Retail: Blockchain enables transparent supply chains for retailers, enhancing product provenance, reducing counterfeiting, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Logistics and Shipping: Blockchain streamlines shipping operations, provides real-time visibility into cargo movements, and reduces paperwork and delays.
Challenges and Future Trends
While blockchain holds immense promise for supply chain management, several challenges remain to be addressed:
- Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility between different blockchain platforms is crucial for seamless integration within the supply chain.
- Scalability: Scaling blockchain solutions to accommodate the demands of large-scale supply chains requires robust infrastructure and efficient processing capabilities.
- Regulation: Clearer regulatory frameworks are needed to guide the adoption and implementation of blockchain technology in supply chains.
- Education and Training: Businesses and individuals need access to adequate education and training to understand and effectively implement blockchain solutions.
Looking ahead, blockchain is poised to transform the future of supply chain management. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) with blockchain, creating intelligent and interconnected supply chain ecosystems. Moreover, the increasing adoption of blockchain in developing countries will facilitate economic development and enhance global trade.
The Metaverse and Blockchain Integration
The metaverse, a collective term for immersive digital environments, has emerged as a groundbreaking technological frontier, promising to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. At the heart of its potential lies the seamless integration of blockchain technology, a transformative force that can address fundamental challenges and unlock new possibilities.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, offers a robust framework for managing digital assets and interactions within the metaverse. By leveraging blockchain, metaverse platforms can achieve greater transparency, security, and interoperability.
Unlocking the Potential of Digital Ownership
One of the most significant benefits of blockchain integration is the ability to establish secure and verifiable ownership of digital assets. Through non-fungible tokens (NFTs), users can own unique digital items, ranging from virtual real estate and avatars to rare digital collectibles and in-game items.
This ownership is not confined to individual users; it extends to virtual businesses and economies. Blockchain empowers the creation of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), allowing for collective ownership and governance of metaverse spaces and assets.
Enhancing Security and Trust
The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for central authorities, fostering a trustless environment. Transactions are recorded on a distributed ledger, making them tamper-proof and auditable. This inherent security is crucial for metaverse applications, where transactions involve valuable digital assets and sensitive user data.
Moreover, blockchain-based identity systems can enhance user privacy and security. Users can control their digital identities and manage data access without relying on centralized intermediaries.
Fostering Interoperability and Decentralization
Blockchain technology facilitates interoperability between different metaverse platforms, allowing users to seamlessly transfer their digital assets and identities across various virtual worlds. This creates a more connected and vibrant metaverse ecosystem, fostering collaboration and innovation.
Furthermore, blockchain promotes decentralization, empowering users to participate in the governance and development of the metaverse. Decentralized marketplaces and communities can emerge, fostering a more equitable and user-centric virtual environment.
Building a Sustainable Metaverse Economy
Blockchain integration enables the creation of robust and sustainable metaverse economies. Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols can facilitate lending, borrowing, and trading within the virtual world, fostering economic activity and liquidity.
By leveraging smart contracts, metaverse platforms can automate transactions, simplify the exchange of goods and services, and create new revenue streams for creators and users.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain technology is essential for realizing the full potential of the metaverse. By addressing core challenges related to security, ownership, interoperability, and economic sustainability, blockchain unlocks a future where virtual worlds are more transparent, secure, and user-centric.
Enhanced Security and Data Privacy

In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the security and privacy of data is paramount. With the ever-increasing volume of sensitive information being shared online, organizations must take proactive steps to safeguard their assets and protect their users. This article will delve into the key aspects of enhanced security and data privacy, exploring the latest trends, best practices, and emerging technologies that are shaping the future of cybersecurity.
The Importance of Data Privacy
Data privacy is not just a legal requirement but a fundamental right. Individuals have the right to control their personal information and prevent its unauthorized use. Organizations have a responsibility to protect this data, ensuring transparency and accountability in their handling of sensitive data. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other similar regulations have established stringent guidelines that companies must comply with to ensure data privacy.
Key Security Measures
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to prevent data breaches and safeguard sensitive information. Some of the key strategies include:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, enhances account security.
- Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest prevents unauthorized access even if the data is intercepted.
- Access control: Implementing access controls ensures that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information, limiting the potential for data breaches.
- Regular security audits: Conducting regular audits helps identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are effective.
- Employee training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices is essential to prevent human error, which is often a key factor in data breaches.
Emerging Technologies
Advancements in technology are constantly evolving the security landscape. Emerging technologies like:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-powered security solutions can detect and respond to threats in real-time, improving threat detection and response capabilities.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can enhance data security by providing a tamper-proof record of transactions, ensuring data integrity.
- Zero-trust security: Zero-trust models assume that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict authentication and authorization at every stage of access.
The Future of Security and Data Privacy
The future of security and data privacy will be driven by a continued focus on innovation and adaptation. Organizations must remain vigilant in implementing the latest security measures, staying ahead of emerging threats. As technology advances, so too will the methods employed by attackers. By embracing proactive security practices, organizations can effectively protect their assets and foster a secure and trustworthy digital environment for their users.
Growth of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)

Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a significant force in the blockchain landscape, offering a new paradigm for organizing and managing organizations. DAOs are essentially digital organizations that operate on a blockchain, governed by rules and code rather than a centralized authority. The growth of DAOs has been fueled by several key factors, including advancements in blockchain technology, the rise of the decentralized finance (DeFi) movement, and the increasing appeal of their decentralized nature.
One of the primary drivers behind the growth of DAOs is the advancement of blockchain technology. Blockchain provides a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger, which is essential for the operation of DAOs. The use of smart contracts on blockchain allows DAOs to automate their operations, reducing the need for traditional intermediaries and human intervention. This automation enables DAOs to operate more efficiently and transparently, eliminating potential issues related to human error or corruption.
The DeFi movement has played a crucial role in fostering the growth of DAOs. DeFi applications have demonstrated the power of decentralized finance, enabling users to access financial services without relying on traditional institutions. DAOs have emerged as a natural extension of DeFi, allowing for decentralized governance and community participation in financial activities. For example, DAOs can be used to manage investment funds, provide decentralized lending platforms, or facilitate the creation of new financial instruments.
The decentralized nature of DAOs has also been a major driver of their growth. DAOs operate independently of any single entity, with decisions being made through a consensus mechanism among members. This decentralized governance structure fosters transparency and accountability, as all actions are recorded on the blockchain for everyone to see. Additionally, DAOs allow for global participation, enabling individuals from diverse backgrounds to contribute to and benefit from their activities.
DAOs have already made a significant impact in various sectors, including finance, gaming, and social activism. They are being used to create new forms of investment, governance, and community engagement. The continued development of blockchain technology, the expansion of the DeFi ecosystem, and the increasing demand for decentralized solutions are likely to further fuel the growth of DAOs in the coming years. As DAOs evolve and mature, they have the potential to revolutionize the way organizations operate and interact with their members.
Cross-Chain Interoperability

In the decentralized finance (DeFi) space, interoperability between different blockchains is crucial for unlocking the full potential of the ecosystem. Cross-chain interoperability enables the transfer of assets, data, and functionalities between different blockchains, creating a more interconnected and unified DeFi landscape.
The Need for Interoperability
The current blockchain landscape is fragmented, with various blockchains offering unique features and advantages. However, this fragmentation also creates limitations. For instance, users might be restricted to interacting within a single blockchain, limiting access to various DeFi services and opportunities.
Cross-chain interoperability addresses this challenge by enabling the flow of value and information across different blockchains. This allows users to access the best features and functionalities offered by various chains, creating a more comprehensive and interconnected DeFi ecosystem.
Types of Cross-Chain Solutions
There are various approaches to achieving cross-chain interoperability. Some prominent methods include:
1. Bridges
Bridges act as intermediaries that facilitate the transfer of assets between different blockchains. They typically involve locking the original asset on one chain and minting an equivalent token on the destination chain. This ensures the security and integrity of the transfer process.
2. Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps allow for the direct exchange of digital assets between two blockchains without the need for a central intermediary. This method relies on a secure and atomic transaction that ensures the exchange is completed successfully or fails entirely, preventing any loss of funds.
3. Cross-Chain Protocols
Cross-chain protocols are decentralized platforms that enable communication and interaction between different blockchains. These protocols typically employ smart contracts to facilitate asset transfers, data sharing, and other functionalities across chains.
Benefits of Cross-Chain Interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability brings numerous advantages to the DeFi ecosystem, including:
1. Enhanced Liquidity
By connecting different blockchains, interoperability facilitates the flow of liquidity across chains, increasing the overall liquidity of the DeFi ecosystem.
2. Access to a Wider Range of Services
Users gain access to a wider range of DeFi services and opportunities offered by various blockchains, expanding their investment and trading options.
3. Increased Efficiency
Cross-chain interoperability enables faster and more efficient asset transfers, reducing the need for cumbersome processes and delays.
4. Enhanced Security
By leveraging the security mechanisms of multiple blockchains, cross-chain solutions enhance the overall security of the DeFi ecosystem.
Challenges of Cross-Chain Interoperability
While offering significant advantages, cross-chain interoperability also faces certain challenges:
1. Security Concerns
Ensuring security is paramount in cross-chain solutions, as any vulnerabilities could lead to significant financial losses.
2. Scalability Issues
As the number of transactions increases, scalability becomes a critical factor in ensuring the smooth functioning of cross-chain solutions.
3. Interoperability Standards
The lack of standardized interoperability protocols can create challenges in integrating different blockchains seamlessly.
Future of Cross-Chain Interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability is a rapidly evolving field with immense potential to transform the DeFi landscape. Ongoing research and development are focused on addressing current challenges and developing more secure, efficient, and scalable cross-chain solutions. As the DeFi ecosystem matures, interoperability will play a pivotal role in fostering innovation and driving the adoption of decentralized finance.
Sustainable Blockchain Solutions

The blockchain, a revolutionary technology, has garnered significant attention for its potential to transform various industries. Its decentralized nature, enhanced security, and transparency have paved the way for innovative solutions. However, the environmental impact of blockchain has become a pressing concern. The energy-intensive nature of traditional blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, has raised questions about their sustainability.
As the world strives for a greener future, sustainable blockchain solutions have emerged as a crucial area of focus. These solutions aim to minimize the environmental footprint of blockchain technology while preserving its core benefits. By adopting innovative approaches, developers and researchers are working towards creating more eco-friendly blockchains that can contribute to a sustainable future.
Key Drivers of Sustainable Blockchain Solutions
The growing awareness of the environmental impact of blockchain technology has spurred the development of sustainable solutions. Key drivers behind this movement include:
- Environmental Concerns: The high energy consumption associated with PoW blockchains has raised concerns about their sustainability. The need to reduce carbon emissions and promote a greener future has become a top priority.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of blockchain technology. Regulations and policies are emerging to promote the development and adoption of sustainable solutions.
- Market Demand: Consumers and businesses are becoming more conscious of their environmental footprint. They are demanding sustainable products and services, including blockchain solutions.
Sustainable Blockchain Solutions: A Focus on Energy Efficiency
The pursuit of sustainable blockchain solutions revolves around reducing energy consumption and promoting energy efficiency. Several key approaches are being explored:
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus Mechanisms
PoS is a consensus mechanism that replaces the energy-intensive mining process with a system where validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold. This significantly reduces energy consumption compared to PoW.
Energy-Efficient Mining Hardware
Advances in hardware technology are leading to the development of more energy-efficient mining equipment. This allows miners to process transactions with less energy consumption.
Renewable Energy Sources
Utilizing renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power for blockchain operations can significantly reduce carbon emissions. This approach promotes a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix for the blockchain industry.
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and rollups, can process transactions off-chain, reducing the load on the main blockchain network and decreasing energy consumption.
The Future of Sustainable Blockchain Solutions
The development of sustainable blockchain solutions is an ongoing process. As research and innovation continue, we can expect to see even more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly blockchain networks. The future of blockchain lies in its ability to evolve and adapt to the evolving needs of a sustainable world.

